Training Consultancy
Comprehensive Training Development Services
On this page, I offer a wide range of services tailored to support every aspect of training development. I provide expert guidance to ensure your projects are efficient and goal-oriented. Each service below is backed by extensive experience and professional knowledge to meet your organization’s unique goals.
Project Coordination
To ensure the success of training development projects, I provide comprehensive project management support. This includes clearly defining project objectives, aligning stakeholder expectations, and establishing a detailed plan that serves as a roadmap for the project.
- Tasks, timelines: Breaking down the project into actionable steps with realistic deadlines.
- Roles, responsibilities: Assigning clear ownership for each task to ensure accountability.
- Communication channels: Setting up efficient communication methods for seamless collaboration.
- Resources: Identifying and allocating the necessary tools, materials, and support for the project.
Quality Assurance and Process Optimization
Ensure high standards with regular checks, quality protocols, and workflow optimization to improve efficiency and maintain consistency.
- Establishing and maintaining quality standards throughout the project.
- Conducting regular checks to ensure compliance and consistency.
- Refining workflows to reduce errors, improve efficiency resource allocation.
Automation and Technical Optimization
Automate e-learning workflows, manage content creation and LMS updates to speed up development.
- Selecting the right content creation tools for the objectives.
- Scripts to accelerate development timelines.
- Implementing automated checks for quality compliance.
- Automating course uploads, updates, and maintenance in the LMS.
Training Needs Assessment
Methods of Training Needs Analysis
Training needs analysis is a crucial process for identifying the skills and knowledge gaps within an organization. Several methods can be employed to assess these needs effectively, including surveys, group discussions, and interviews.
- Online Survey: A widely used method to gather quantitative data from a large number of respondents, helping to identify common learning needs.
- Focus Group Discussion: A qualitative method where a small group of participants share insights, providing a deeper understanding of training requirements.
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations with key stakeholders to gather detailed, personalized information about training needs.
- Objectives from Managers: Managers provide insights into organizational goals, helping to align training with business priorities.
- Desk Reviews of Documents and Policies: Analyzing existing materials to identify potential gaps in current training programs and policies.
Skill Gap Analysis
Skill gap analysis identifies the disparity between the skills employees currently possess and those required to achieve organizational goals. This process helps in planning targeted training programs to address the identified gaps.
- Assessment of Current Skills: Evaluates the existing capabilities of employees through surveys, tests, or performance reviews.
- Identification of Future Requirements: Determines the skills needed to meet upcoming challenges or strategic objectives.
- Comparison and Analysis: Highlights discrepancies between current skills and future requirements to prioritize training needs.
- Action Planning: Develops a structured plan to bridge the identified skill gaps through training or recruitment.
Job Role Mapping
Job role mapping aligns employee roles with organizational goals by defining responsibilities, required skills, and performance expectations. It ensures clarity and consistency in job functions across the organization. Job role mapping builds on skill gap analysis by structuring the skills and responsibilities required for each role, creating clear and well-defined expectations.
- Role Definition: Identifies and outlines key responsibilities and deliverables for each job role.
- Skill Matching: Maps necessary skills and competencies to specific roles for optimal performance.
- Performance Benchmarking: Establishes standards and metrics for evaluating role-specific success.
- Training Alignment: Connects identified skill gaps to targeted learning initiatives to enhance role effectiveness.
Instructional Design
Method Selection
Choosing the right instructional methods is essential for effective learning, ensuring the approach aligns with both learner needs and content complexity. A few examples of these learning methods:
- Microlearning
- E-learning (static, dynamic)
- Blended learning
- Instructor-Led Training (ILT)
- Workshops
- Simulations
- Game-Based Learning
- Social Learning
- On-the-Job Training (OJT)
- Instructional Videos
- Animated Explainer Videos
Key considerations for method selection include:
- Audience Analysis: Understanding learner demographics, preferences, and prior knowledge.
- Content Complexity: Evaluating the depth and breadth of the material to determine the method's adequacy.
- Learning Objectives: Aligning the method to specific outcomes, such as skill acquisition or behavioral change.
- Technological Infrastructure: Ensuring compatibility with available tools and platforms.
- Engagement Potential: Selecting methods that actively involve learners.
- Cost and Resources: Balancing effectiveness with budget and time constraints.
Curriculum Development
Curriculum development involves creating structured learning paths that effectively address the learning needs of individuals or teams.
- Learning Objectives: Clearly define the desired outcomes to ensure the curriculum aligns with organizational and learner goals.
- Module Selection: Identify core topics and break them into focused modules or blocks tailored to address specific skills or knowledge areas.
- Pathway Design: Combine modules into flexible short-term courses or comprehensive long-term learning plans based on complexity and priorities.
- Scalability: Design paths to accommodate diverse learner groups, from beginners to advanced levels.
Microlearning
Microlearning is a focused and flexible learning approach that delivers bite-sized, easily digestible content tailored to meet specific learning objectives. It enhances retention and engagement by providing learners with concise, actionable knowledge when and where they need it.
- Short Learning Modules: Content is broken down into manageable, focused segments that learners can quickly absorb.
- On-Demand Access: Provides learners with the flexibility to engage with materials anytime, anywhere.
- Multimedia Formats: Incorporates videos, infographics, quizzes, and other engaging formats to support diverse learning preferences.
- Application-Oriented: Focuses on practical knowledge and skills that can be immediately applied in real-world scenarios.
- Retention and Engagement: Regularly reinforces key concepts to enhance memory and sustain interest.
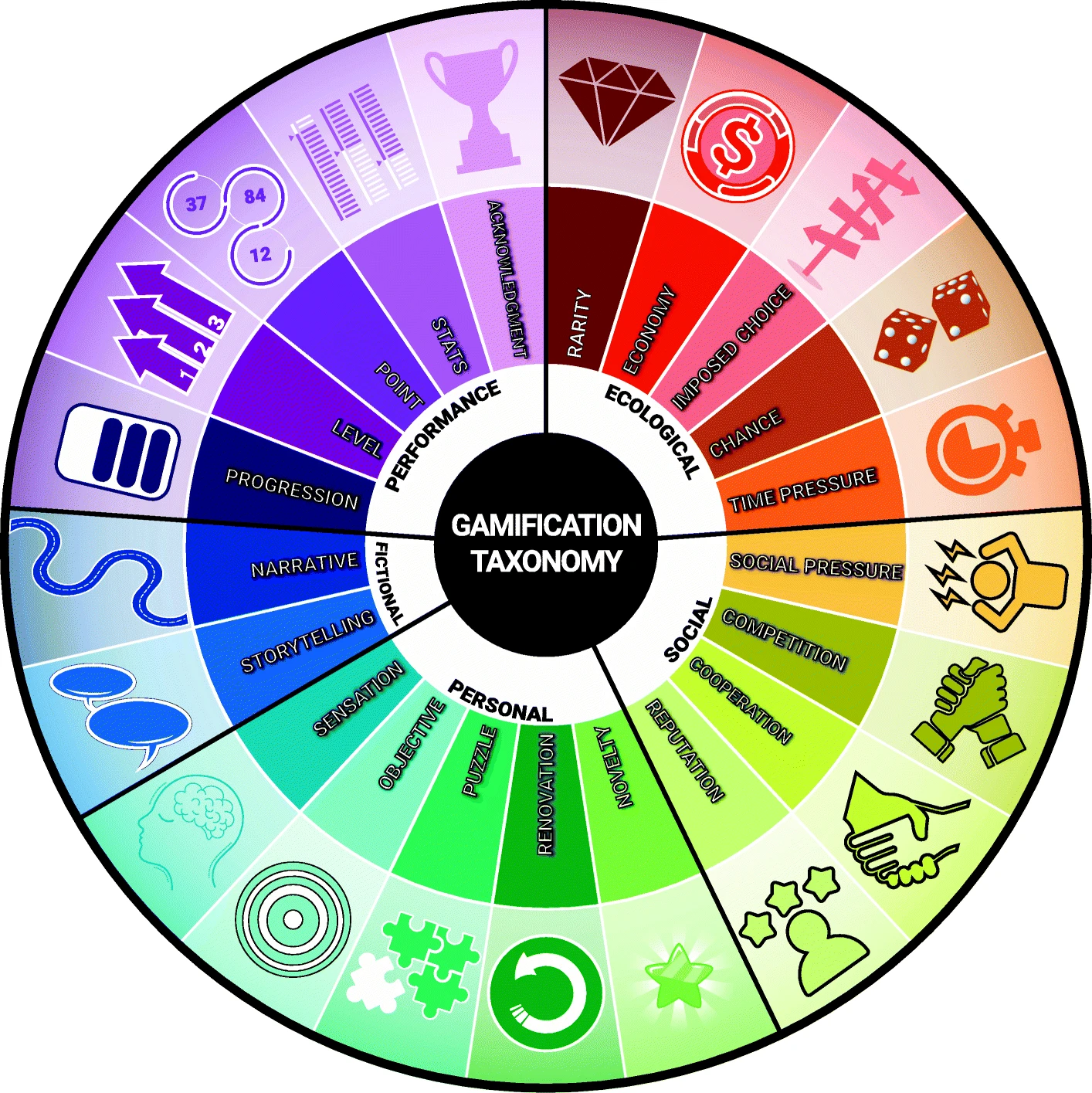
Gamification
Gamification is the integration of game-like elements into non-game environments, enhancing engagement and motivation. By using mechanics like points, levels, and rewards, gamification encourages active participation and progress tracking. Key methods include:
- Progression: Displays the learner's journey, often through progress bars or maps.
- Points and Levels: Learners earn points (XP, HP, KP) and advance to higher levels with more challenging tasks.
- Acknowledgement: Badges, medals, and achievements serve as external feedback for learner actions and accomplishments.
- Social and Competition: Promotes interaction through leaderboards, teams, and social challenges to foster collaboration or healthy competition.
 Gamification tools
Gamification tools
Learning Content Development
E-learning Development Tools
Choosing the right e-learning development tools is critical for creating engaging and effective digital learning experiences. These tools vary in features, complexity, and cost, so selecting the right one depends on specific project requirements and constraints.
Key considerations for selecting an e-learning development tool:
- Ease of Use: Tools should match the technical expertise of the development team to ensure efficiency.
- Compatibility: Support for SCORM, xAPI, or other standards for LMS integration.
- Interactive Capabilities: Ability to create quizzes, simulations, branching scenarios, or multimedia-rich content.
- Customization: Flexibility in design to align with branding and learner needs.
- Cost: Balancing features against budget, including subscription or licensing fees.
- Support and Updates: Access to customer support, tutorials, and regular updates.
- Output Formats: Ensuring compatibility with devices (desktop, mobile, tablets) and offline availability if required.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Articulate 360: Versatile, beginner-friendly suite with multiple tools but requires high licensing costs.
- Adobe Captivate: Advanced features for simulations but steep learning curve.
- iSpring Suite: Easy PowerPoint integration but less creative freedom for complex designs.
- Camtasia: Excellent for video tutorials but lacks advanced interactivity features.
- H5P: Free and open-source but limited in advanced customization options.
- Vyond: Perfect for animated explainer videos but may require higher budget for premium features.
Comprehensive Educational Video Production
An expertly crafted educational video encompasses a wide range of professional services. These include project management, instructional design, scripting, storyboarding, staging, on-site directing, lighting, filming, sound engineering, editing, color grading, closed-captioning, motion graphics (2D, 3D, or special effects), animation, location and props coordination, casting, and narration. Each element is carefully executed to meet your specific learning objectives.
Our educational videos can serve various purposes, including:
- Expert interviews or “talking head” videos
- Simplified explainers
- Demonstrations of models, topics, or activities
- Showcasing best practices and work methods in real-life settings
- IT system tutorials with screen recordings
- Internal communications or organizational profile overviews
- Promoting corporate programs
- Virtual backgrounds or virtual studio production using chroma key (green screen)
- Scenario-based or gamified training videos
 Showcase: Instructional video for UNHCR
Showcase: Instructional video for UNHCR
Explainer Animation Video Creation
Explainer animation videos are an effective way to simplify and clarify complex ideas by using visuals, animations, and voiceovers. They engage learners by presenting information in a fun and easy-to-understand manner.
When creating explainer videos, there are several professional considerations to keep in mind:
- Audience Understanding: Tailor the animation style, tone, and complexity of the content to meet their needs, knowledge level, and preferences.
- Message Clarity: Deliver a clear and concise message without overloading the audience with details. The script should be straightforward, and visuals should support, not distract from, the core message.
- Storytelling: Use a compelling narrative with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Define a problem, present a solution, and end with a call to action or takeaway.
- Visual Consistency: Match the animation style to the video's tone and content and also to the branding. Consistent colors, fonts, and character design create a professional and cohesive look.
- Length and Pacing: Keep the video short (1-3 minutes) and use pacing to emphasize key points and transitions. Avoid unnecessary details to keep the message clear and quick.
- Sound Design: Ensure the voiceover is clear and professional, and background music complements the tone without distracting from the message.
 Exapmle: Exlainer Animation Video
Exapmle: Exlainer Animation Video
Digital Adoption Platforms (DAP)
A Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) is an automated software layer integrated between an Enterprise Application Software (EAS) and its users. It facilitates learning, onboarding, and adaptation during new software implementation or updates, providing real-time guidance and analytics to enhance user experience and software effectiveness.
- Key Applications: Supports user training, onboarding, and smooth adoption of new or updated software.
- Real-Time Learning: Enables task-based learning during real-time operations.
- Guides: Offers in-app, interactive, step-by-step, and context-sensitive instructions.
- Analytics: Tracks user activity to inform data-driven training development or software improvement.
- Targeted Support: Adapts to varying levels of user experience to ensure personalized assistance.
Adaptive Learning
Adaptive learning delivers personalized educational experiences tailored to the unique needs of each learner. Leveraging algorithms and artificial intelligence, it dynamically adjusts to interactions, providing support and guidance to enhance the learning process.
- Scaffolding Support: Transitions learners from passive information processing to active collaboration through tailored cognitive aids.
- Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT): Questions are classified by difficulty, with each subsequent question calibrated to match the learner's current ability level.
- Hints and Feedback: Context-sensitive tips appear to assist learners, especially in the event of errors.
- Collaborative Learning: Groups participants based on shared interests to foster cooperative learning experiences.
- Simulations: Uses complex conditions to create adaptive, real-world scenarios for practical learning.
Implementation
Learning Management Systems
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are powerful online platforms designed to streamline training and education processes. I assist in selecting, customizing, and deploying LMS solutions to meet your organization’s unique needs, ensuring a seamless learning experience for both administrators and learners.
- Core Features:
- Admin functions: Manage user registrations, assign courses, and track progress.
- Learner interfaces: Provide access to training materials, quizzes, and interactive modules.
- Reporting tools: Generate detailed analytics and progress reports.
- Content Management: Organize and upload diverse training materials, from videos to documents, ensuring easy access for learners.
- Additional Services: Incorporate classroom training records, performance appraisal systems, and 360-degree feedback tools.
Implementation in E-Learning
The implementation phase in e-learning involves launching and managing the training program to ensure a seamless and effective learning experience. This phase focuses on delivering content, preparing training coordinators, and supporting learners throughout the process.
- Content Deployment: Uploading and configuring e-learning modules on the learning management system (LMS) for easy access by participants.
- Technical Setup: Ensuring all platforms, tools, and devices are tested and ready for use, minimizing potential disruptions.
- Pilot Testing: Conducting trial runs of the course to identify and address any content or technical problems.
- Learner Support: Providing ongoing assistance, such as FAQs, live chat, or helpdesk services, to ensure participants can navigate the e-learning environment smoothly.
- Feedback Collection: Gathering initial learner impressions and technical performance data to refine and optimize the program in real-time.
Implementation in Traditional Training
The implementation phase in classroom training involves delivering the program while coordinating all logistical and organizational elements.
- Material Distribution and Logistics: Preparing and providing printed handouts, manuals, or other training materials to participants. Setting up training tools, devices, and any necessary supplies to the location.
- Trainer Preparation: Ensuring instructors are fully briefed on the training objectives, session flow, and available resources.
- Logistical Arrangements: Coordinating with the venue on room setup, seating plans, and technical requirements such as projectors, microphones, and Wi-Fi.
- Participant Support: Organizing catering or meal plans, ensuring dietary requirements are addressed, and providing clear instructions for arrival and parking.
- On-Site Coordination: Overseeing day-of activities, such as registration, timekeeping, and troubleshooting unexpected issues.
Evaluation
Learning Analytics and Reporting
Learning analytics and reporting involve measuring, collecting, analyzing, and reporting data related to students and their context to understand and optimize learning and the learning environment. It typically involves displaying this information through learning dashboards, which visualize learning data using various data visualization tools.
Common use cases include identifying effective educational techniques, forecasting at-risk students, personalizing learning pathways, and enhancing instructor effectiveness. The data often includes click patterns, navigation trends, time spent on tasks, test results, and HR-related data, such as job roles and team structure.
Methods for Measuring Training Effectiveness
When measuring the effectiveness of a training program, various methods are used to assess different levels of impact. These methods help determine how well the training has achieved its objectives at each stage of learning. Common measurement methods include:
- Reaction: Measures participant responses on training content, methods, trainer effectiveness, learning conditions, and attitude change.
- Learning: Includes quizzes, multiple-choice questions, simulations, skills checklists, and semantic differential surveys to assess knowledge, skills, and attitudes before and after training.
- Behavior: Involves questionnaires, follow-up interviews, performance evaluations, and direct observation to analyze behavioral changes and performance outcomes.
- Results and ROI: Assesses organizational impact through surveys, interviews, and cost-benefit analysis, measuring productivity, customer satisfaction, and financial or human resource outcomes.
Assessing Training Effectiveness with Experiments
Various experimental methods can be used to assess the effectiveness of training programs:
- Social Experiment (Participants vs. Non-participants): This method allows for full control over the selection process but can be challenging due to the difficulty of excluding individuals and potential uncontrolled interactions between groups.
- Association (Quasi-experiment) (Statistical Pair Comparison): A statistical comparison of paired groups before and after training, useful for minimizing bias from hidden variables, but requires extensive data collection.
- Before-and-After Comparison: A simple and data-light method to compare results before and after training, although environmental changes may impact the findings.
- Difference-in-Differences (DID) (Participants vs. Non-participants): This approach compares the changes in both groups to account for hidden variables, but requires pre- and post-training data collection from both groups.
- Cross-Sectional (Post-training average compared to control group): This method compares post-training results between groups, unaffected by environmental changes, but also requires data collection after training.

